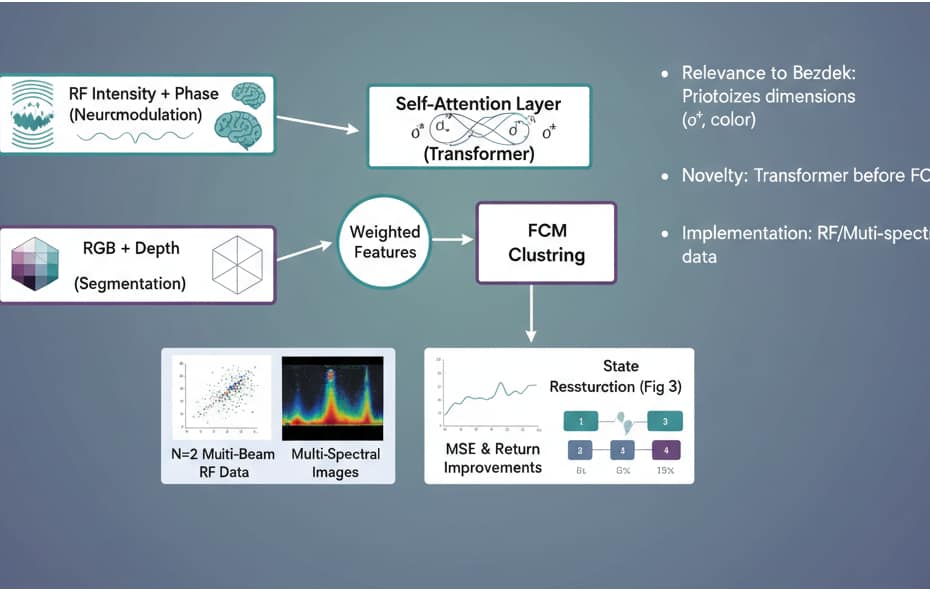
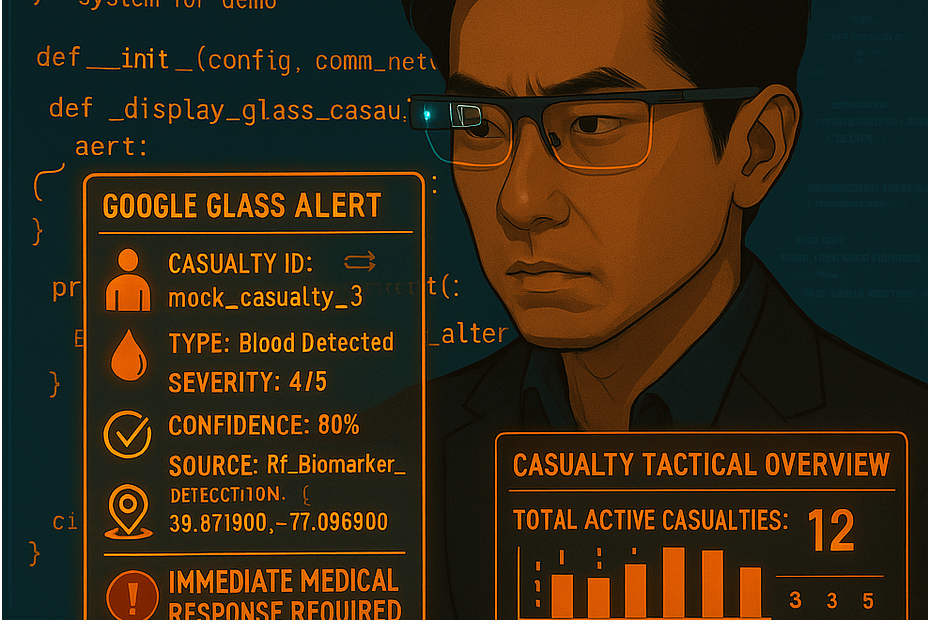
QuestDB + CrateDB as Dual-Store Telemetry Backbone: Performance Benchmarking and Cost Analysis
Modern distributed systems generate massive volumes oftelemetry data requiring both real-time processing and longterm analytical storage. Traditional single-database approachesstruggle to optimize for conflicting requirements: time-seriesworkloads demand high ingestion throughput and temporalqueries, while analytical workloads require… QuestDB + CrateDB as Dual-Store Telemetry Backbone: Performance Benchmarking and Cost Analysis