SCYTHE Recon Chaos Shared, Persistent, Operator-Grade Brain
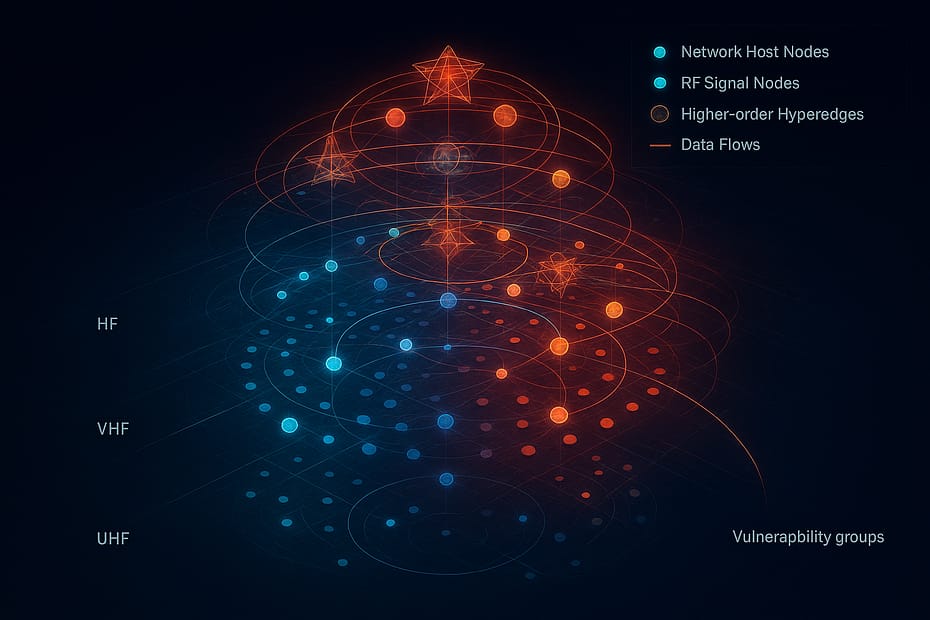
Podcast: There’s a moment in every serious system build where you stop adding features and start eliminating entropy. That’s what this SCYTHE milestone was about: taking a fast-growing recon stack—entities, sensors, missions, signal intel, live… SCYTHE Recon Chaos Shared, Persistent, Operator-Grade Brain